Collagen Fibers: Where Are Collagenous Fibers Found? (+ Definition)

Many of our first introductions to collagen products start online. Whether they are mentioned by our favorite influencers who swear by this miracle protein for their stunning complexion and jaw-dropping good looks or wellness professionals who cannot start their morning routine without a scoop in their smoothie.
It's hard to deny all of the incredible benefits that taking a collagen supplement can have on our skin, let alone our joints, bones, and muscles. In fact, there are numerous studies that have shown that consuming collagen can help slow down and reverse signs of aging throughout the body and especially in our skin.
But, we can almost guarantee that the average collagen consumer doesn’t know how collagen plays a part in our skin. This tiny protein physically gives shape and resilience to all of our tissues, including our blood vessels. As a matter of fact, all of our connective tissues consist of tiny collagen fibers that are much stronger than what meets the eye. They provide support, structure, and strength to everything from our muscles and joints to our skin.
What Is Collagen?
Before we get into what collagen fibers are, we should get a better understanding of what collagen actually is.
Nowadays, most people have heard of collagen because it appears in almost everything, from skincare to smoothies. But, there’s more to collagen than its anti-aging properties. Collagen is the most abundant protein in our tissues and makes up almost 35% of the total protein content within the human body.
Despite all of the collagen foods, supplements, creams, and treatments on the market, you may be surprised to learn that our bodies naturally produce collagen molecules on their own.
To produce collagen, we need special cells called fibroblasts which are located in the extracellular matrix of our connective tissue. Collagen consists of three amino acids, glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. These three amino acids, or alpha peptides, are twisted together to make a long right-handed triple helix.
A collagen’s unique triple helix shape is what makes it so important to our cells and tissues. This unique shape:
- Provides strength and structure
- Prevents enzymes from breaking it down
- Allows collagen to be bonded with other cells
- Helps with tissue regeneration, making it essential for forming the extracellular matrix of our various tissues
We can thank our fibroblasts for forming and twisting these alpha peptides together to create a molecule called procollagen. Procollagen contains more amino acids than collagen proteins and these extra amino acids are referred to as amino acid residues. Once the amino acid residues on either end of the molecule are removed, procollagen can become collagen. These individual collagen molecules then become “trimers” in the endoplasmic reticulum. Molecules like sugar, hydroxyl groups, and sulfide-sulfide bonds are added to select amino acids throughout the polypeptide strands (or alpha peptides) before they go on to become collagen fibrils, and later collagen fibers—but we’ll get to that later.
When we refer to collagen, it’s easy to think that there is just one type of this structural protein. However, there are about 15 different collagen types and each type has its own important role in the human body.
What Are Collagen Fibers? (Definition)
So, what are collagen fibers exactly? You can think of collagen fibers as the rope within your tissues.
From afar, rope looks like one tough, solid (but flexible) material. But up close, it's easy to see that rope is made up of many smaller, thinner fibrous strands that have been woven and intertwined together to form one continuous, sturdy cord. And, because they are braided, ropes are able to resist tensile forces, meaning that they can be stretched or stressed without breaking.
Just like rope, a collagen fiber is made up of a bunch of smaller collagen fibrils. Collagen fibrils are made up of a bunch of even smaller collagen molecules.
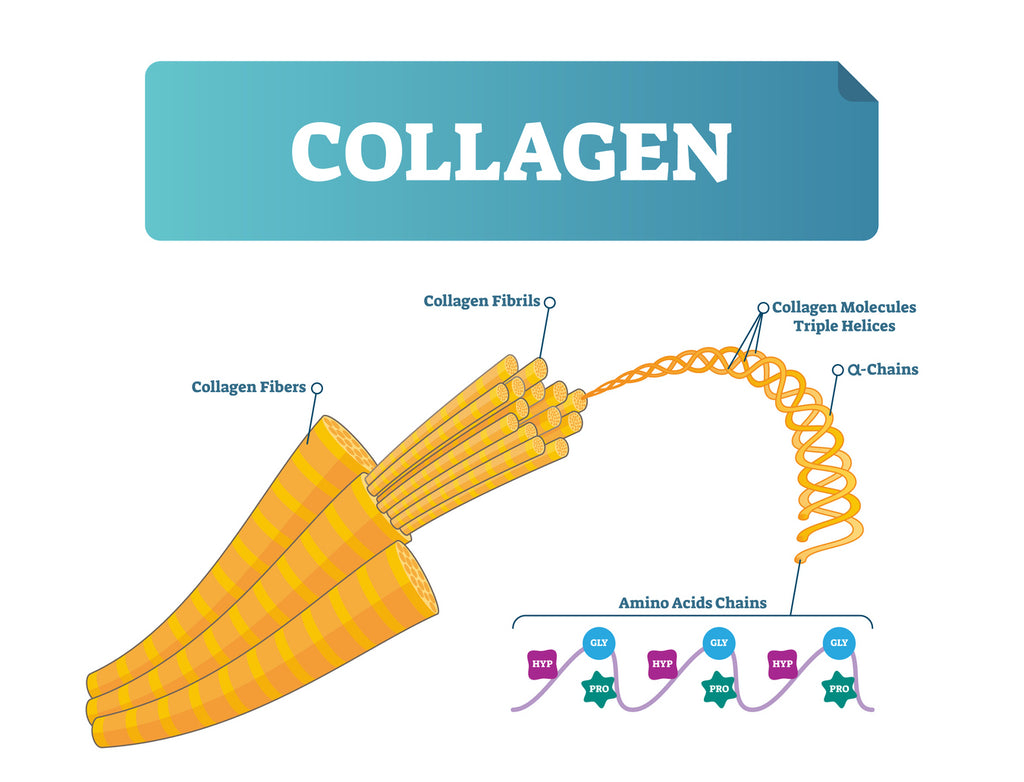
How are collagen fibrils formed exactly? When a collagen molecule is synthesized by our fibroblasts, the individual, right-handed triple helix collagen molecule will bond together with other collagen molecules and assemble tight bundles called collagen fibrils. Due to the molecular structure of the collagen molecules, they are able to use covalent cross linking to stabilize and strengthen their bond with other collagen molecules. You can think of covalent cross-links as little knots that tie all of the collagen molecules together.
The way that our collagen fibrils are arranged in our collagen fibers is what makes them incredibly strong and able to endure a variety of tensile forces while providing structure to our connective tissue and skin.
Depending on where the collagen fibers are located in the body, such as in bones, tendons, muscles, dermis, or other areas, they can vary in length. And, depending on the tissues where the elastic fibers are located, the number and density of collagen fibers in an extracellular matrix can differ, but we’ll explain that in-depth later.
What you may be able to gather from all of this information is that we have to take care of our existing collagen fibers for healthy skin, muscle, and connective tissue function. Taking a dietary supplement like Taut Collagen Powder is the best way to get in your daily dose of collagen peptides and give your collagen fibers an extra boost of support.
Our collagen powder is perfect for those of us who are always on the go. Each sachet contains 2,500mg of hydrolyzed marine collagen peptides along with hyaluronic acid and grape seed extract to prevent and reverse premature skin aging, improve moisture levels within the dermis, and support healthy, bouncy, radiant skin.
Normal collagen molecules are too large for our body to absorb, which is why we use a revolutionary patented hydrolysis technology that breaks down each collagen molecule into individual particles known as collagen peptides. Your skin is able to then use these collagen peptides more efficiently to trigger collagen production.
This isn’t your ordinary collagen peptide powder supplement, our formula has a unique fast-acting formula that dissolves quickly, bypasses any digestive processing, and enters your bloodstream within minutes to get straight to work. We call this the “Rapid Delivery System” and this ensures that you and your skin can absorb all of the benefits that are packed into each sachet.
Simply pour one sachet into a glass of water or directly onto your tongue. For people between the ages of 20 and 49, we recommend taking 2 to 4 sachets of collagen powder per day (that’s up to 6,000mg of collagen peptides). For people over the age of 50, we recommend taking up to 10 sachets per day. You can also combine our collagen powder with our Taut Collagen Drinks.
What Are the Different Types of Collagen Molecule? (4 Major Types)
As we mentioned above, there are about 15 different types of this abundant protein in our body, however, not all of the collagen types are equally represented in our tissue, blood vessels, cartilage, bone, and skin. In fact, there are four major types of collagen. Let’s take a look at the four major types and the functions they have in the body:
- Type I collagen – Type I collagen is the most commonly found of all of the different collagen types throughout the human body. Type I collagen is a major component in the skin, cartilage, bone, connective tissue, nails, hair, and teeth. This collagen is fibrillar, meaning that its fibers give structure to our connective tissues, bones, and other parts of our body. 1
- Type II collagen – Type II collagen is a protein that’s mostly present in our bone, cartilage, and connective tissues. Many collagen supplements that support weak bones and joints have high concentrations of type II collagen. Type II collagen may also help reduce pain and swelling throughout the body. 2
- Type III collagen – Type III collagen is an extracellular matrix protein that is present in our organs, blood vessels to regulate blood pressure, and muscles. In fact, type III collagen makes up to 20% of the collagen content in the body. 3
- Type IV collagen – This type of collagen is mostly found in the skin, specifically in the basement membranes. Unlike most of the other collagen types, this type does not have the amino acid glycine. Glycine is what makes the collagen helix tight, even though it is the smallest amino acid without a side chain. Since this collagen molecule doesn’t have glycine, the collagen’s triple helices are more flexible and pliable, allowing them to create sheets within the cutaneous basal lamina of the dermis. 4
By now you can probably tell how big of a role collagen plays in the health and vitality of almost everything in our body, especially within the dermal layer of our skin. In fact, there have been many studies suggesting that taking the right kind of collagen supplement can help lessen the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging, for plump, supple, and healthy-looking skin.
A hydrolyzed collagen supplement, like Taut Liquid Collagen Drink, can visibly reduce signs of aging caused by environmental toxins, UV damage, and particles from mast cells by not only providing the dermis with a highly absorbable form of collagen (type I collagen and type III), but also by triggering your fibroblasts to boost collagen production on their own. 5
How Does Taut Liquid Collagen Work?
When you drink a bottle of Taut Collagen, the high percentage of nano-sized hydrolyzed collagen peptides enter your bloodstream within seconds. Once your body detects the 13,000mg of collagen peptides, it naturally activates the wound healing and repair response. As a result, the fibroblasts within the extracellular matrix of your dermis produce type I collagen to increase its overall collagen density. When used frequently over time, you’ll start to see results like firmer, fuller, radiant, and more youthful skin.
While the main component of this powerful drink is collagen that has been harvested from wild-caught red snapper from the Indian Ocean, the drink’s unique formula also contains other skin-loving active ingredients like elastin peptides, hyaluronic acid, grape seed extract, vitamin C, ceramides, vitamin B6, and salmon DNA. Together, these active ingredients improve the moisture content in the dermis, strengthen the epidermis, protect the collagen fibers within the dermis from free radical damage, support collagen fibers and elastic fibers, and stimulate fibroblasts to increase collagen production.
What Are Diseases That Affect Collagen Fibrils & Fibers?
To give you an example of how important collagen fibers are, we can look at a condition like Ehlers Danlos syndrome. This gene mutation affects around 1 in 5000 people and can cause a range of connective tissue defects due to the effects it can have on type I, type III, and type V collagens. People who have inherited this syndrome usually have very thin, inelastic skin, fragile tissues, weak bones, and loose joints that typically bend more than they should.
Another condition related to collagen is osteogenesis imperfecta, a gene mutation that can affect type I collagen. People with this mutation have bones that can break and fracture easily because their bones are not formed properly. This just goes to show how big of a role collagen fibers play in the body and why we need to maximize their longevity.
Where Are Collagen Fibers Found? (Extracellular Matrix)
Our bodies are made up of many different kinds of connective tissue. Cartilage, bone, tendons, ligaments, and fat are all different forms of connective tissue. You can also find dense connective tissue in the dermal layer of the skin. We rely on connective tissue to give structure, support, and a framework to the other tissues and organs in our bodies.
What is connective tissue made of? Our connective tissues consist of four major components: collagen fibres, elastic fibers, ground substance, and cells.
Collagen fibres play an important role in the cells of our connective tissue, they are the most abundant protein in our extracellular matrix after all. They help support the cell’s various functions like migration, proliferation, cell adhesion, and metabolism. 6
Beyond the function of collagen fibers at a cellular level, they also are essential for providing structure and support. You can think of each collagen fiber as a pillar or beam that helps support a house.
Apart from physically supporting our tissues, collagen fibrils and fibers affect the mechanical properties of the tissue that they are in. Individual fibers can be arranged in a variety of combinations and concentrations, depending on the tissue’s function in the body.
For example, in our tendons, collagen fiber makes up to 85% of the extracellular matrix. Because the fibers are densely packed together, they allow for our tendons to resist tensile forces and connect our bone to our muscle without breaking or tearing. 7
Collagenous fibers within the extracellular matrix of our dermis naturally affect the mechanical properties of our skin, determining how it responds to stress and strain. Each and every collagen fiber is aligned to form a mesh-like structure within our dermis. This is how our skin is able to move, stretch, and bounce back the way that it does. It’s like a big rubber band! 8
Why Do We Need More Collagen?
As we mentioned earlier, our bodies naturally start to slow down collagen production as we get older. That means that after the age of 20, we start to produce 1 to 2% less collagen every year. And, for us women, collagen production slows down even more during and after menopause. Unfortunately, the bad news gets even worse. Not only does our collagen production slow down, but our collagen levels naturally deplete over time.
You can think of our collagen levels as a water balloon. When we’re young, our water balloon is completely full and this is when our skin is its most youthful, plump, and glowing. However, once we hit our 20s, a tiny needle makes a hole in our water balloon. At this point, we are able to continue filling up our balloon and the damage is not completely visible. Although, over time, the hole from the needle expands and water rushes out of the balloon faster than we are able to refill it. This causes the balloon to look saggy, empty, and dull. We hate to say it, but the same goes with our skin.

What Damages Collagen Fibers in Our Skin & Connective Tissue?
Several factors can be depleting your collagen levels without you even knowing it! Besides getting older, there are a few lifestyle habits that can trigger premature collagen loss in men and women:
High Sugar Diet
We’re sure you’re just like us and love the occasional sugary treat when the mood strikes. The reality is, eating a high-sugar diet can damage the collagen and elastic fibers in your skin and connective tissue, which can lead to premature aging.
How can a cookie cause you to age prematurely? It all boils down to a process called glycation. When you eat too much sugar and your sugar levels are high, a process called glycation is triggered which then produces Advanced Glycation End Products, or “AGEs” for short.
AGEs are harmful byproducts that can stick to a collagen fiber and damage it by making it stiff. Not only that, but AGEs can alter the stability of a collagen molecule, making it more prone to damage.
Smoking
We all know the many dangers of smoking cigarettes, but many people are unaware of the impact that smoking can have on the dermis, cartilage, bone, and other connective tissues.
The issues that come along with smoking can be attributed to the many chemicals found in cigarettes. These chemicals can have a direct impact on the collagen and elastic fibers throughout the body.
Studies have shown that cigarette and tobacco use affects the rate at which collagen fibers are produced in the extracellular matrix of your skin which leads to sagging, wrinkles, and fine lines. Tobacco use can even cause vertical wrinkles and hyperpigmentation around your mouth, otherwise known as “smoker’s lips.”9
Smoking can also reduce blood flow throughout your tissues. One study showed that heavy smokers had a thicker endothelial basal lamina and an accumulation of fibronectin in their veins when compared to non-smokers. These abnormalities can impact the function of the blood vessels and lead to further health issues down the road. 10
Sun Exposure
The more time we spend out in the sun, the more we are exposing our dermal cells to UV radiation. The sun’s UV rays are one of the biggest contributors to our exposure to free radicals. While free radicals sound like something that you would find marching for peace in the 60s, they’re actually a type of unstable oxygen molecule that has only one electron instead of two.
To make up for their missing electron, they scavenge the body for cells, including the collagen fibers in our skin and the rest of our body, to damage them at a molecular level. What is a free radical? RenewSkin Inc. explains. 11
When our cells are damaged and aren’t able to function properly, we can experience oxidative stress. This is when diseases, accelerated aging, and even cancer start to creep up on us. Fortunately, there are ways to prevent or slow the progression of oxidative stress by increasing our intake of antioxidants. Research has shown that antioxidants are able to prevent tissue damage related to free radicals by giving them some of their own electrons, effectively neutralizing them. 12, 13
You may have seen “A Rich Source of Antioxidants” advertised on some of your favorite foods, but these little molecules are no sales gimmick. There are many foods that contain antioxidants, like berries, broccoli, artichokes, and chocolate, but one of the best ways to get enough antioxidants in your diet is by taking an effective supplement, like LAC Masquelier’s French Pine Bark.
These powerful tablets contain French Pine Bark Extract and Original Oligomeric Proanthocyanidins, or OPCs, which have been shown to be significantly more effective as antioxidants than both vitamin E and vitamin C. Not only can these antioxidants neutralize free radicals and toxins, but they can also protect your vascular system and enhance blood flow to naturally remove waste from the tissues and cells throughout your body.
Just 1 to 2 tablets per day can also provide potent support to your collagen fibers and protect them from free radical damage so you can maintain healthy collagen levels and rejuvenate your skin, joints, and connective tissues.
How to Support Your Collagen Fibers (Collagen-Rich Foods & Supplements)
These are three of the most common ways that you can counteract collagen loss and increase collagen fiber within your connective tissues:
Collagen-Rich Foods
Can you really improve your skin through your diet? Besides lowering your intake of processed foods and sugar, eating foods rich in collagen and protein can help you maintain healthy collagen levels. As we've discussed, collagen consists of various amino acids (glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline). Eating a diet high in protein can support collagen synthesis with your cells. Some of the best foods for the collagen fiber in your skin and connective tissues include:
- Bone broth
- Gelatin
- Eggs
- Fish
- Meat
If you’re a vegan or vegetarian and follow a diet that doesn’t include any animal products, some of the best foods that you can eat to support collagen synthesis are:
- Avocados
- Citrus fruits
- Berries
- Leafy greens
These foods contain vitamins and nutrients like zinc, copper, and vitamin C which promote collagen production within your cells and protect your existing collagen fiber from free radical damage.
Topical Skincare Products
If you walk the aisles of your local drug store, you’ll notice almost every brand features its own spin on a collagen cream that promises to smooth out your wrinkles and tighten sagging skin. While many of these creams will hydrate your skin, they won’t necessarily reverse the clock. This is because many of the collagen products on the market contain large collagen molecules that cannot be absorbed by our dermis and reach our dermal cells.
When choosing a topical collagen product, always keep your eyes peeled for formulas containing hydrolyzed collagen. Just like collagen liquid or powdered supplements, topical skincare products should also contain hydrolyzed collagen so that your body is able to better absorb and utilize the nano-sized molecules.
Hydrolyzed collagen is a very safe protein that can provide deep moisturizing properties when applied to the dermis. And, hydrolyzed collagen also has natural antioxidant properties that can help stabilize free radicals within the dermis to prevent damage to your dermal cells. 14
However, unlike liquid and powdered versions of this supplement, topical products won’t increase your collagen levels. So, if you’re trying to support the collagen fiber within your bone and cartilage, topical skincare products won’t provide the benefits that you’re looking for.
Collagen Supplements
One of the best ways to support the collagen fibers in your cartilage, bone, dermis, and connective tissue is by taking a collagen supplement. Collagen supplements are sourced from the connective tissue of animals. Unfortunately for the vegans and vegetarians out there, there are no natural sources of collagen peptides that are sourced from plants.
While shopping for collagen supplements there are a few of attributes that you should look out for:
- Hydrolyzed collagen - The most effective collagen supplements use hydrolyzed collagen peptides since collagen molecules are too large to be absorbed by the body.
- Marine collagen - The source of your collagen peptides is important for maximum results. Marine collagen derived from wild-caught red snapper or cod is rich in type I and type III collagens, which are the most abundant collagen types in your connective tissue and dermis. Marine collagen is derived from the connective tissues of fish like the skin, scales, and bone.
- High potency - The higher the collagen content, the sooner you’ll start to see noticeable benefits. To support the collagen fiber in your dermis, we recommend taking more than 10,000mg of collagen type I and III per day.
- No fillers - In order to best support your collagen fibers, you should look for a supplement that doesn’t contain any additional additives or fillers.
You can find collagen supplements in three main forms: liquid, powder, and capsule. Liquid and powder supplements are the most common because they are the easiest to take and often contain a higher amount of collagen peptides.
Strengthen Your Collagen Fibers From Within With Ms. Magnifique
You’ve seen how big of a role collagen fibers play in keeping your tissues (and your skin) strong and healthy. While we can’t do much about the natural aging process, we can take measures to support our existing collagen levels.
That is exactly why we’ve created the Ms. Magnifique Transformation Program. This program bundle contains three of our most effective and revitalizing products so you can support your collagen fibers from the inside-out and the outside-in.
Each bundle contains 3 boxes (a 24-day supply) of our luxurious Taut Collagen Liquid Drink to provide your dermis with the highest-quality Type I and Type III collagen peptides for visible and immediate results.
To further support the quality of your skin and collagen fibers, this bundle includes our Taut Bright Bye Bye Dark Spots, our daily brightening supplement. This antioxidant-packed pill contains 5 active ingredients that have been backed by science to provide incredible results: L-glutathione, L-cysteine, grape seed extract, artichoke leaf extract, and olive leaf extract. These ingredients protect our skin and collagen from cellular damage to inhibit the production of melanin, which can even out the skin and lessen the appearance of age spots.
Last but not least, this transformative bundle comes with 1 box of our Taut Collagen Masks (5 in total). These sheet masks have been formulated to target dehydrated, sagging, and dull-looking skin. The collagen peptide essence contains nano-sized collagen molecules which are small enough to deeply penetrate the skin right into the dermis layer to rejuvenate the skin. The unique and luxurious essence also contains hyaluronic acid, botanical squalene, and antioxidants to instantly tone, hydrate, and brighten your complexion.
Why wait to upgrade your skincare routine? Transform your skin with the best collagen products and your collagen fibers will thank you.
Find out the best Transformation Program for your skin’s needs by taking our skincare quiz!
References:
- Type I Collagen
- Collagen Type Ii (Native) - Uses, Side Effects
- Type III Collagen (COL3A1): Gene Structure, Tissue Distribution, and Related Diseases
- Collagen IV in Normal Skin and in Pathological Processes
- The Role of the Mast Cell in Skin Aging
- Connective tissue
- Collagen structure of tendon relates to function
- Extracellular Matrix of the Skin: 50 Years of Progress
- Smoking affects collagen synthesis and extracellular matrix turnover in human skin
- Is basal lamina thickening in the saphenous vein a smoking hallmark?
- UV Damage of Collagen: Insights from Model Collagen Peptides
- Understanding antioxidants
- Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health
- Collagen Hydrolysates for Skin Protection: Oral and Topical Use